
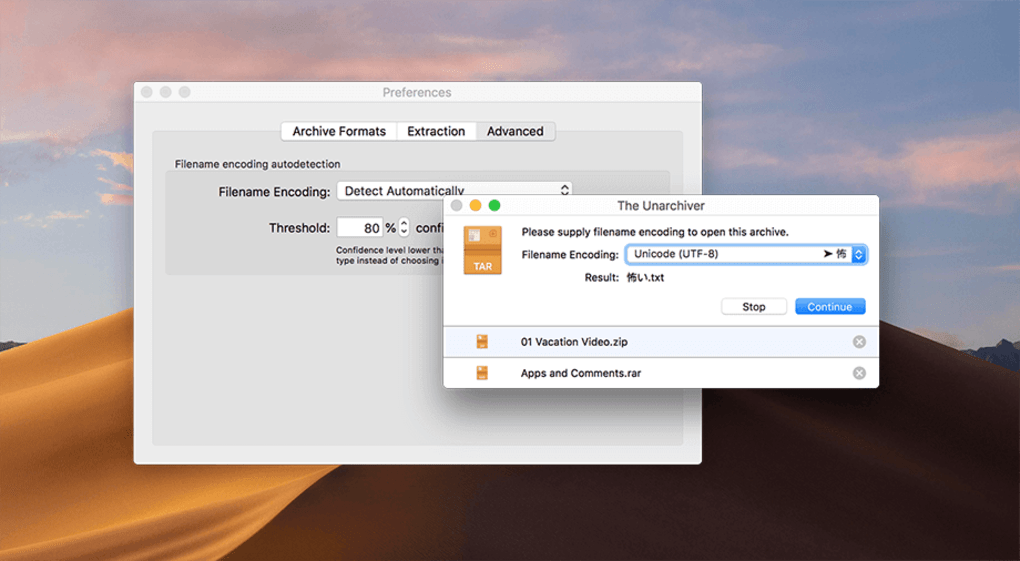
- #UNARCHIVER VS UNRARX MP4#
- #UNARCHIVER VS UNRARX INSTALL#
- #UNARCHIVER VS UNRARX ARCHIVE#
- #UNARCHIVER VS UNRARX RAR#
Users send these files in a folder that contains many documents.
#UNARCHIVER VS UNRARX ARCHIVE#
$ unrar x stands for Roshal Archive compressed files. $ unrar x /media/data/homes-backup.rar homes-backup/ path_to_extract\įor a complete listing of commands and switches simply run:
#UNARCHIVER VS UNRARX RAR#
$ rar a -r -rr10p -s /media/data/homes-backup.rar examples General syntax $ unrar command - switch 1 - switch N archive files. I named it 'home-list' in this example but you can call it anything you want: In this example, the list will be three lines long.
#UNARCHIVER VS UNRARX MP4#
Switches=-m5 -rr5p -ol -s -md64 -msmp3 mp4 avi mkv zip 7z rar tar gz bzip2 zst jpg jpeg gifįor a complete listing and explanation of rar's switches, see rar(1). Switches= any_RAR_switches_separated_by_spaces The syntax of the file is simply the following string: in the user's home directory) or if you wish to define a global set of options for all users, in the /etc directory. RAR for Linux reads configuration information from the file ~/.rarrc (i.e.
#UNARCHIVER VS UNRARX INSTALL#
Alternatively, install unrar for just UnRAR. Install the rar AUR package for both RAR and UnRAR. In newer versions, password protection can optionally protect filenames too, so that the filenames contained within the archive will not be displayed without the right password. The only known ways to recover an encrypted file are via dictionary or brute force attacks. Older versions of the file format used a proprietary algorithm newer versions use the AES encryption algorithm, a block cipher adopted as an encryption standard by the U.S. Most currently used compression formats (with the exception of the older ZIP) allow solid structuring. RAR archives can be of a solid format, in which all of the compressed files are treated as a single data block.RAR does not support tapes, as it uses seek and rename operations on its files. partXXX RAR file, without the need to manually copy and then rejoin the pieces, or for extracting a file from a single piece without needing all pieces. Built-in support for multi-volume files enables the unpacking program to simply prompt the user for the next.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
